-
 News
News -
 People
People -
 Facilities
Facilities -
 Research
Research -
 Active and regenerative shock absorbers
Active and regenerative shock absorbers -
 Active magnetic bearings
Active magnetic bearings -
 AI-based battery modeling and monitoring
AI-based battery modeling and monitoring -
 Autonomous driving and AI for automotive
Autonomous driving and AI for automotive -
 Electric and hybrid powertrains
Electric and hybrid powertrains -
 Electrodynamic bearings
Electrodynamic bearings -
 Mechatronic systems for mountain safety
Mechatronic systems for mountain safety -
 Rotordynamics
Rotordynamics -
 Vehicle dynamics and vehicle architectures
Vehicle dynamics and vehicle architectures -
 Vibration and motion control
Vibration and motion control
-
-
 Collaborations
Collaborations -
 Student Teams
Student Teams -
 Publications
Publications -
 Contact
Contact
Electrodynamic bearings
An Electrodynamic Bearing exploits the eddy current effects that take place in a conductor rotating in a constant magnetic field to achieve levitation without additional devices, as sensors, power electronics, etc.
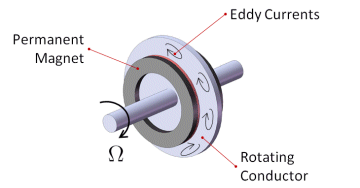
The working principle relies on the motion of a conductor in a magnetic field. Their relative motion causes a variation of the magnetic flux linked to the conductor. It generates an electromotive force that induces eddy currents, which in turn generate electromagnetic forces, that are used to produce the suspension effect.
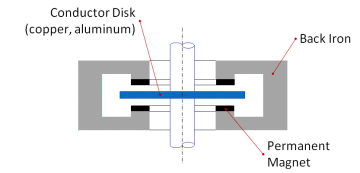
In Eddy Current Systems such as Electrodynamic Bearings, the study of the dynamic behavior is of great importance as these systems are inherently unstable due to the presence of rotating damping. In order to optimize the design procedure a hybrid approach is useful, taking advantage of both analytical and numerical modeling to single out the most important characteristics and predict the behavior of the bearing in operating conditions.Experimental tests are also important to validate the design procedure. The design of a test bench is of main interest expecially to verify the quasi-stationary characteristic of the electrodynamic bearing.
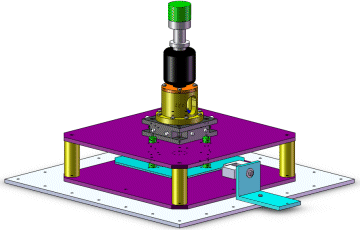
Once optimized, electrodynamic bearings may show to be an interesting solution for very high speed rotating machines such as turbomolecular pumps, energy storage flywheels, vacuum cleaners, etc. The absence of contact and auxiliary systems allow clean and robust operation at costs possibly far lower than traditional AMBs.
